
Abstract This volume explores the growing significance of open public spaces within university campuses—spaces that go far beyond their functional role to become essential arenas for social interaction, informal learning, well-being, and urban integration. Rooted in the research projects LOVE Sapienza and NARRATES both founded by Sapienza Università di Roma, and enriched by contributions from …
Abstract Default contentItaly’s policies for the protection of historical cities in the 1960s and early 1970s met with great praise from European countries and institutions at the time of their implementation. In the following decades, they became a model for architects and planners worldwide and particularly for large international organizations. This article focuses on the …
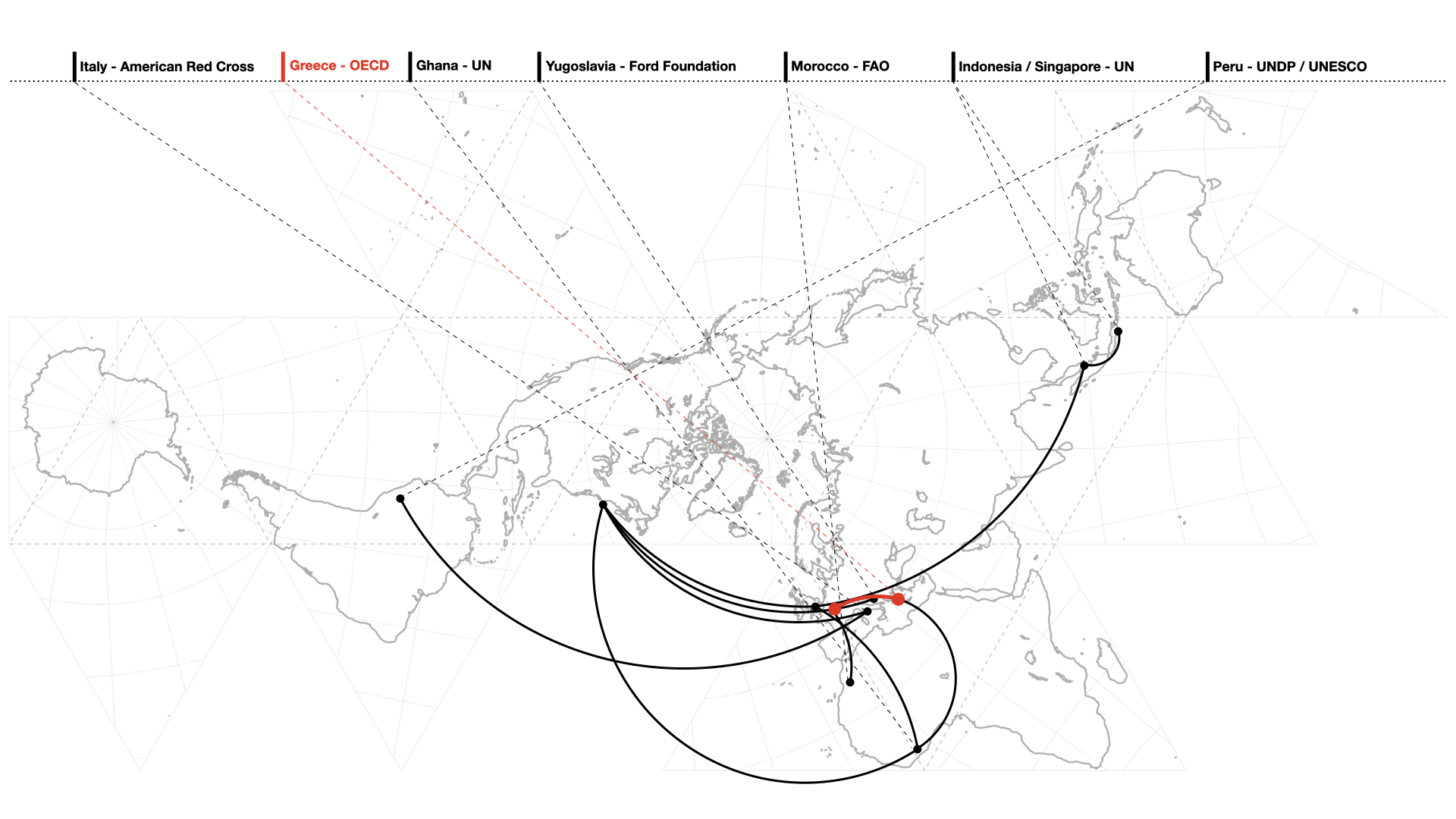
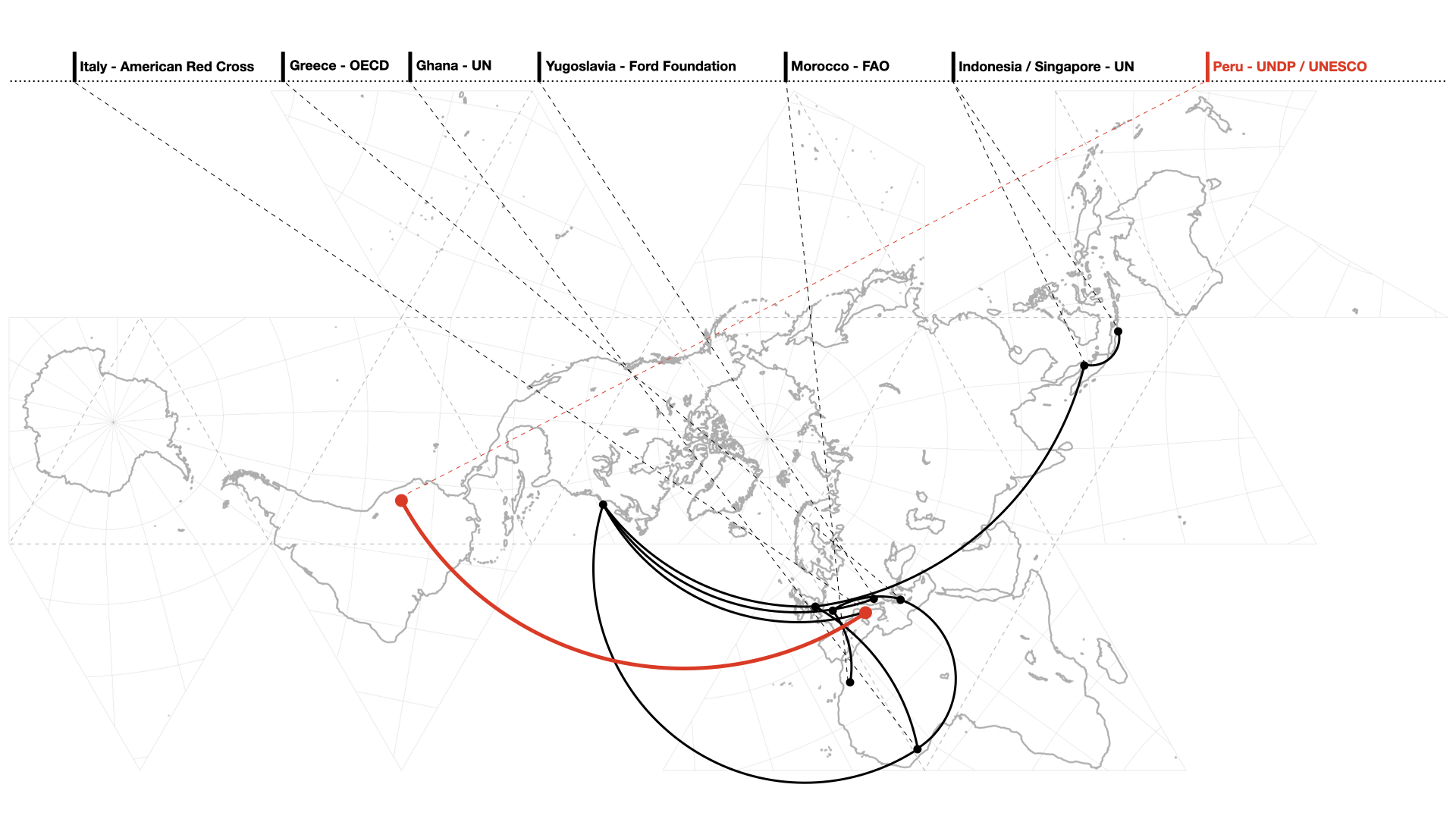
Abstract The Organization for European Economic Cooperation (OEEC) was founded in 1948 with the aim of connecting European countries to the United States through the economic project of the Marshall Plan. Since 1958, the OECD has worked with Greek governments to modernize and develop the country. Part of the investigations undertaken by the OECD in …
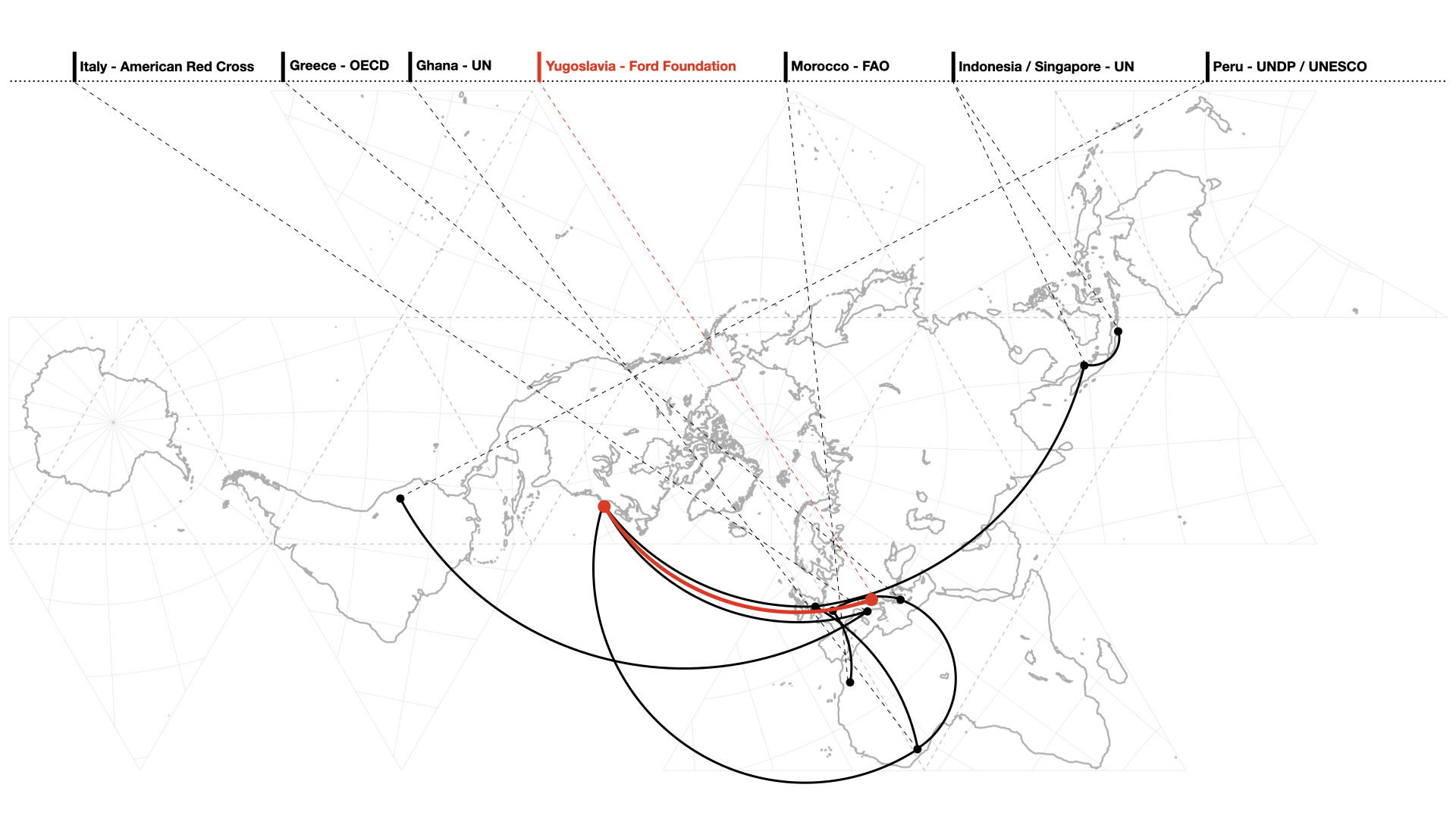
Abstract The article focuses on the American-Yugoslav Project in Regional and Urban Planning Studies (AYP) to explore the Ford Foundation’s role in the international circulation of urban planning expertise during the Cold War. In operation in Ljubljana, Slovenia, 1966–1976, AYP was a foundation-funded collaboration between Ljubljana’s Urban Planning Institute of SR Slovenia and a succession …

Abstract The Monthly Bulletin of Tropical Housing & Planning was founded by Constantinos A. Doxiadis and Jaqueline Tyrwhitt in October 1955. Originally meant to collect professionally useful information on the so-called ‘developing countries’, the publication soon changed its name and scope, becoming an internationally distributed, widely read and highly influential journal dedicated to the science …
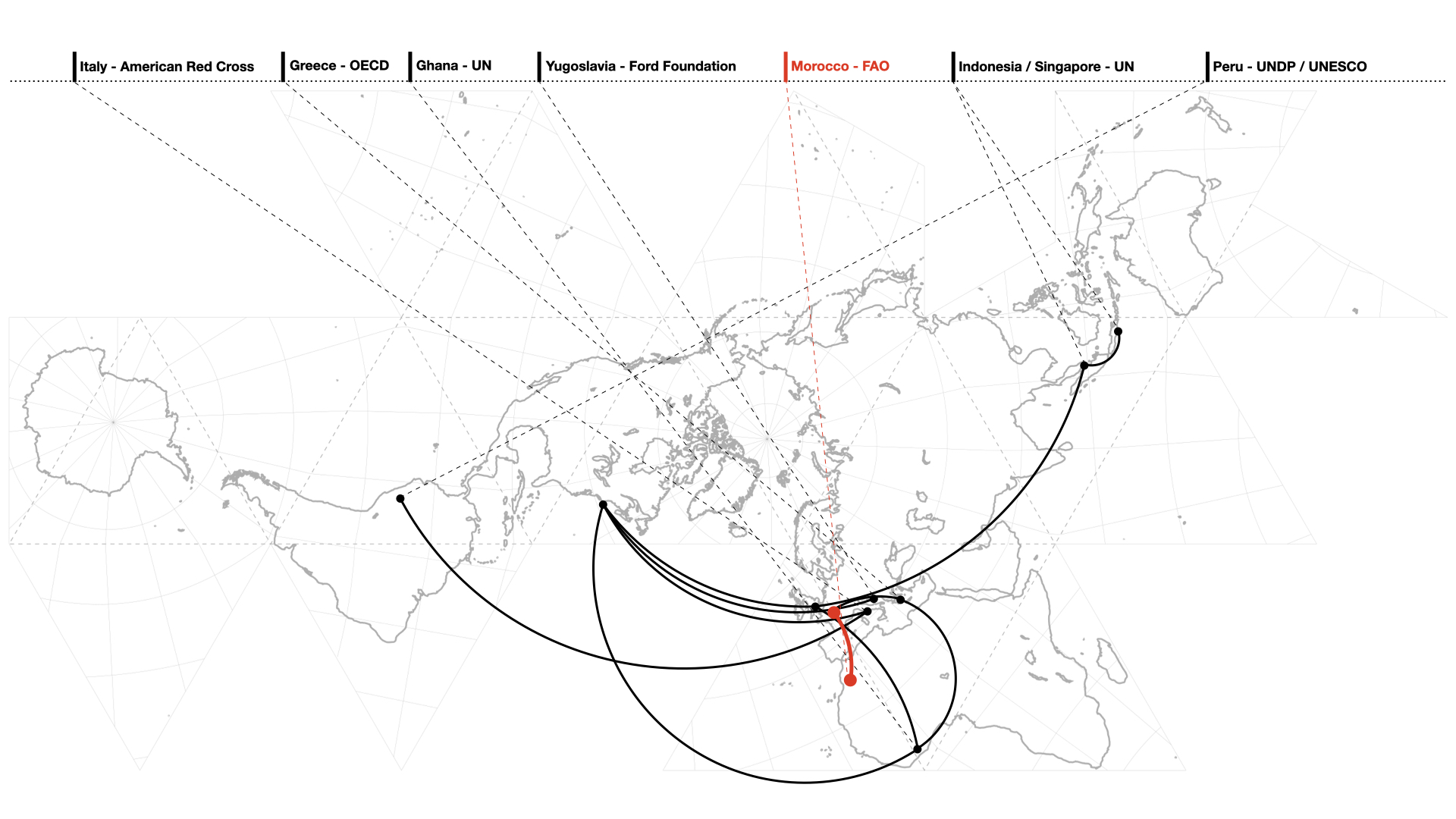
Abstract DDuring the late colonial era and after independence, international organizations engaged in donating foreign aid to Morocco. The United Nations’ technical assistance initiatives engaged in ambitious schemes targeting the rural realm. Among them, the Lalla Mimouna community development project (1957–1965), the Projet Sebou (1963–1980), and the Programme d’habitat rural (1967–1972). All three projects were concerned about the physical …
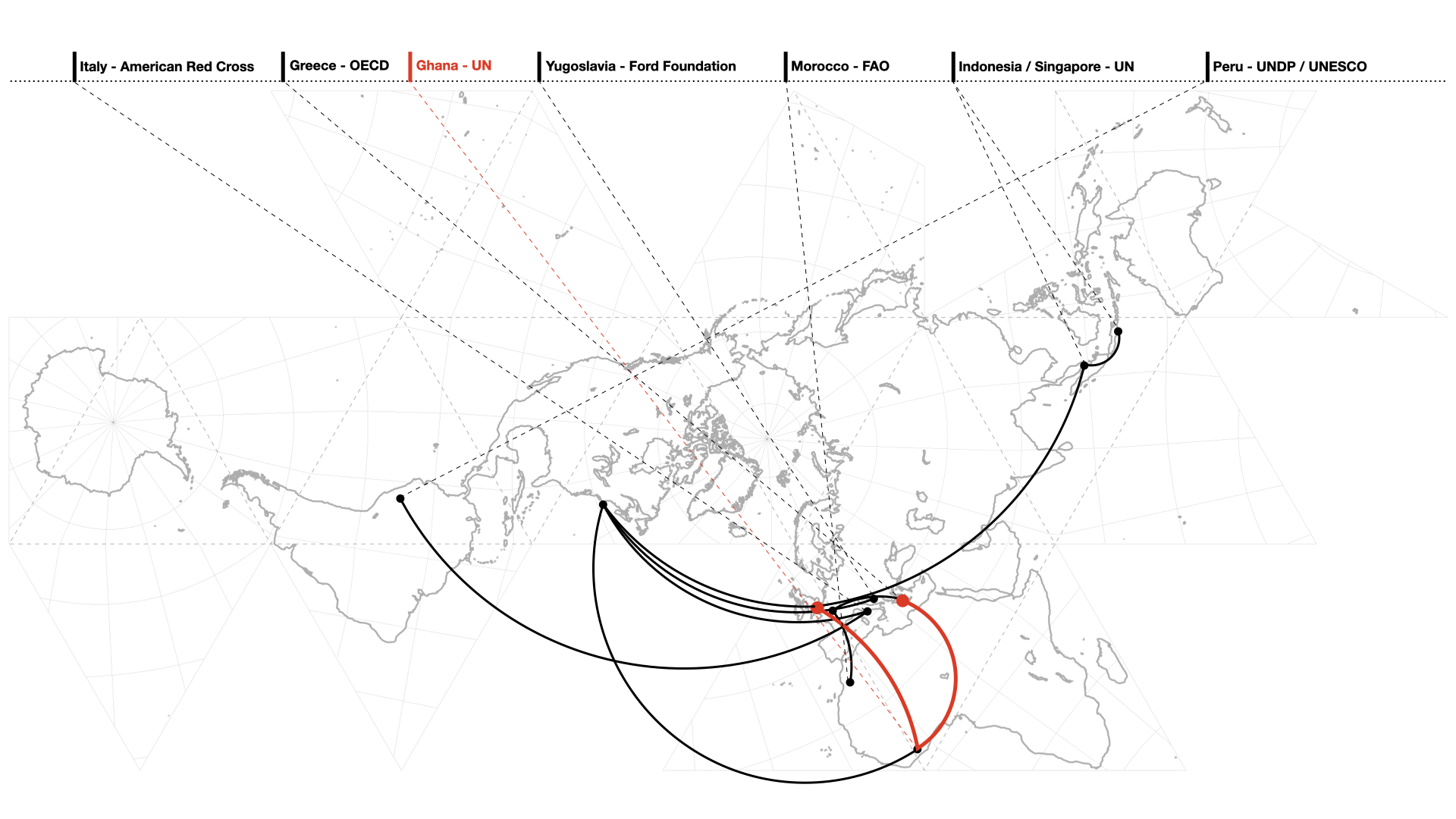
Abstract DIn the early days of the United Nations, the main form of aid in the field of housing took the shape of technical assistance. Although the pool of specialists was almost coincident with those from colonial networks, the ambitions and limitations of international, non-governmental and neutral cooperation implied a reconceptualisation of the world division …
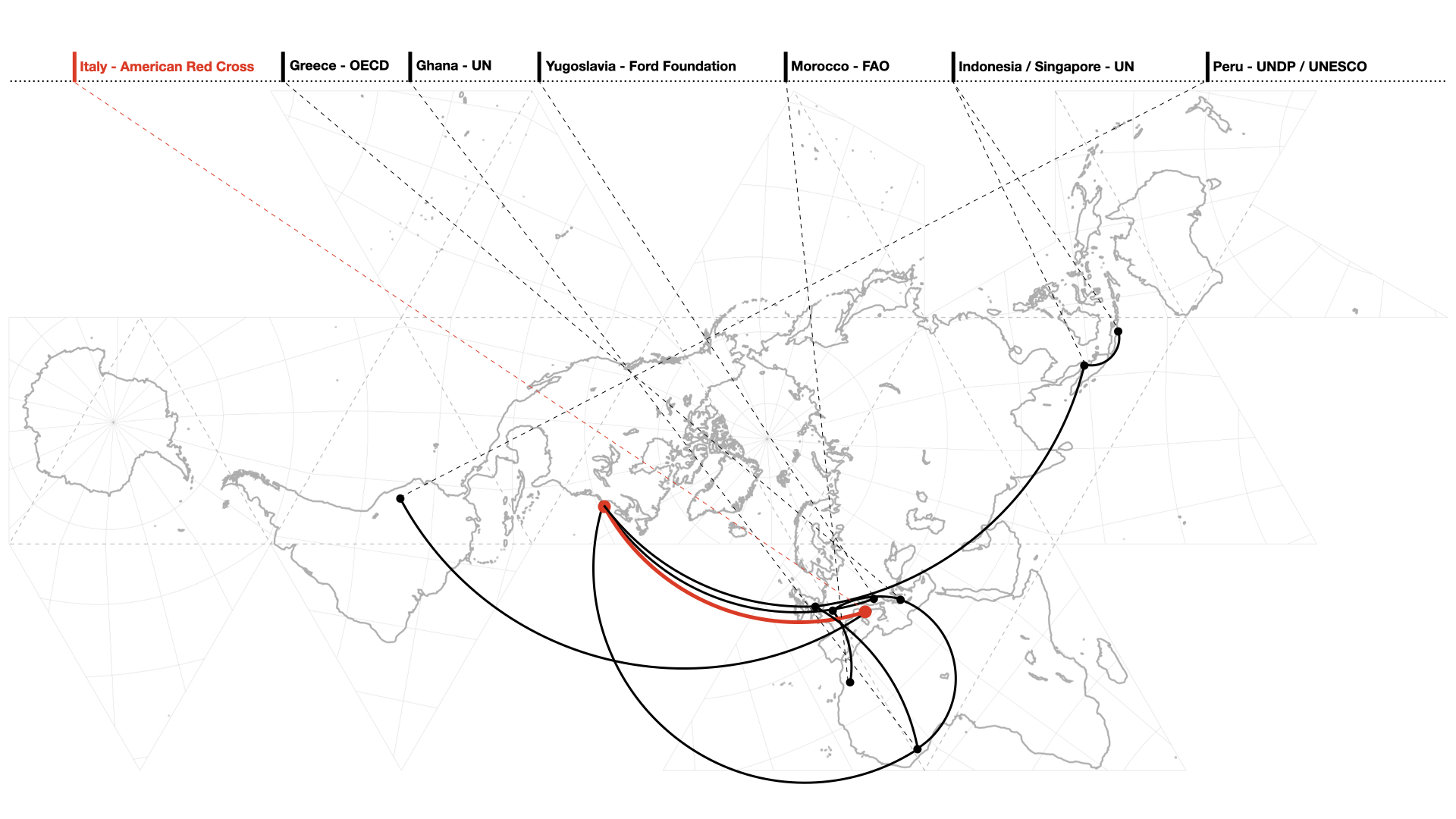
Abstract The article hinges on the important political changes and imperial anxieties that characterized the U.S. at the tail end of the nineteenth century. As the country was attempting to rise to international prominence with military and economic means, it authorized the American Red Cross (ARC) to operate in foreign lands and transmit narratives of …

Abstract After the conferences in Bretton Woods (1944) and San Francisco (1945), and especially with the implementation of widespread technical assistance policies of the Point Four Program (1949), teams of experts composed primarily of architects, but also economists, sociologists and anthropologists, began to gravitate around supranational organizations such as the United Nations, the World Bank …
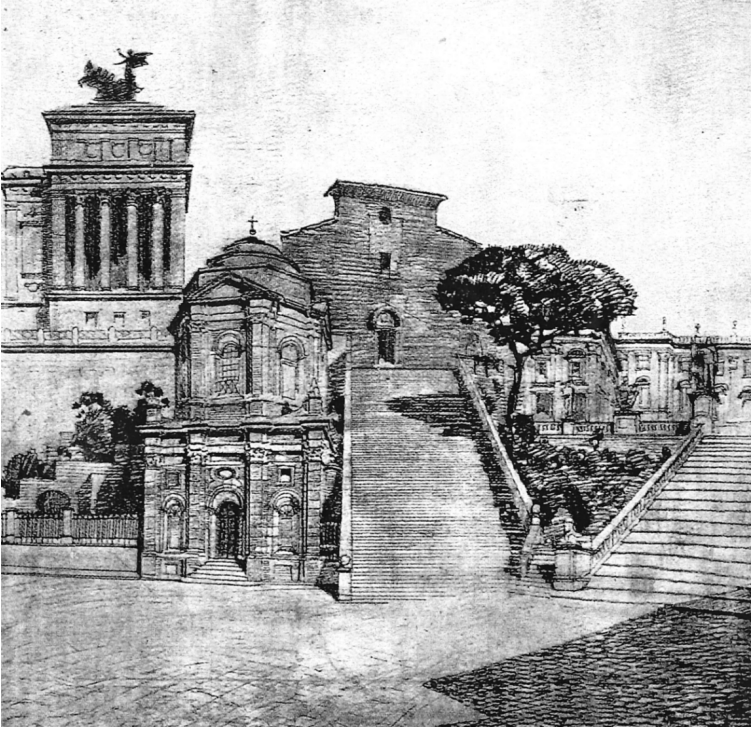

Abstract DThe ‘ambientista’ city of the early twentieth century was a mediated expression of many of Gustavo Giovannoni’s reflections. This paper argues that it can be studied in the light of several earlier events and through numerous archaeological and architectural activities in the newly established capital of Rome. In the progressive definition of the project …










